If you are new to trading it can be difficult to know where to start. Markets are extremely volatile, and even the most experienced traders can get whipsawed by huge price fluctuations.
In times of uncertainty, sometimes it’s a good idea to take a step back and review the fundamentals of trading the markets. In this report, we will start with the basics of Options Trading.
Here’s the material we will cover:
- What are Options
- Which is Better? Trading Stocks or Options?
- What Does it Mean to Buy Call Options
- What Does it Mean to Buy Put Options
- What is Time Decay?
- How Do I Get Started?
What Are Options?
According to Investopedia, the term option refers to a financial instrument that is based on the value of underlying securities such as stocks. An options contract offers the buyer the opportunity to buy or sell—depending on the type of contract they hold—the underlying asset. Unlike futures, the holder is not required to buy or sell the asset if they decide against it. Each contract will have a specific expiration date by which the holder must exercise their option. The stated price on an option is known as the strike price. Options are typically bought and sold through online or retail brokers. (Source: Investopedia)
Each Options contract controls 100 shares of the underlying stock for a specified period of time. The Options contract could expire at the end of the week, it could have a monthly expiration or it could expire several months out.
Which is Better? Trading Stocks or Options?

- They’re too hard to understand.
- They’re too expensive. It’ll cost me far too much money.
- They’re only for professionals with years of experience.
- They take too much time to learn and execute
- Or, 90% of options expire worthless. That’s too much risk for me.
Truth is — once you put the fears to rest with options trading, they can be an invaluable part of your trading strategy.
Look at AT&T (T) for example. Let’s say you bought the stock at its November 6, 2017 low at $32.50. When it ran from a high of $38.50, you made a profit of 18%. Great.
However, had you bought the AT&T February 16, 2018 32.50 call option, which traded at $1.70 on November 6, 2017, you could have made a profit of 212% at $5.30 a contract.
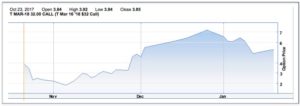
Look at it another way. Let’s say you wanted to buy 100 shares of AT&T at $32.50.
It would cost you $3,250. When it ran to $38.50, you were up a few hundred dollars. At the same time, you could have controlled 100 shares of the same asset for just $170 (or $1.70 x 100 shares in an options contract).
It’s actually very straightforward to understand.
If you think a stock is going up, you buy a call. If you think a stock is going down, you buy a put. An option is a contract that gives a buyer the right but not the obligation to buy or sell a stock, ETF or index.
If you thought AT&T would move higher – as it did – you would buy a call option.
Each of these contracts – which derive value from respective stocks, ETFs or indexes – control 100 shares, and remains good until a set expiration date (third Friday of your chosen strike month, or expiration month).
While stocks are safer with no expiration dates, they don’t afford you the opportunity that options can with simple leverage. Plus, options can often times allow you to spend much less money on a trade than a stock.
They’re not hard to understand. They’re actually cheaper than buying a stock. You did not need years of experience to wrap your head around the trade idea. It doesn’t take long to understand at all.
What Does it Mean to Buy Call Options?
If you believe a stock is going to increase in price over the short term, you can buy a Call Option.
Let’s take a look at the iShares U.S. Aerospace and Defense ETF (ITA)
With war raging in Ukraine, the US and NATO nations have continued to pledge billions of dollars in weapons to help the Ukrainians fight off the Russian invasion. ITA is an ETF that buys a basket of Aerospace & Defense companies including Raytheon, Lockheed Martin, Boeing and Northrop Grumman, among others.

With ITA currently trading at $100.25, let’s assume you believe that it has room to run up to $104.50 in the short term, touching the 200 SMA line, shown in red.
You could invest $10,025 to buy 100 shares of ITA. If you sold at $104.50 per share, your profit would be $425 for roughly a 4 percent return on capital risked.
On July 5, you could have also bought the August 19th ITA Call for $3.26. Since one Options contract controls 100 shares, your total investment would have been $326. If ITA moved as expected up to $105 within a couple of weeks (July 19), then you could exit the trade for a $262 gain (80% return).
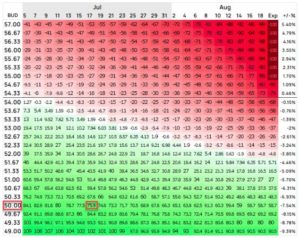
You can use free tools like optionsprofitcalculator.com to calculate the approximate value of your options contract over time.

Image courtesy of optionprofitcalculator.com
On July 5, I plugged in the $100 Option contract for ITA expiring August 19. You can see that the value of the options contract increases by 80.4% if the price of the stock goes up to $105 by July 19.
Options can give you much greater leverage over buying and selling stocks, but you must know how to manage the trades. Time is not necessarily your friend the longer you hold an options contract. As you can see by the diagram above, the value of the options contract erodes over time. This is called Time Decay. More on this later.
What Does it Mean to Buy Put Options?
If you think the price of a stock is going to decrease over the short term, you could choose to buy a Put Option.
Let’s take a look at Anheuser Busch (BUD). Since April, BUD has been on a gradual downtrend, making lower highs and lower lows.

On July 5, BUD was trading at $53.60, but had recently been trading at $50. You could buy a BUD Put Options Contract expiring August 19 for $3.15. Again, one Options Contract controls 100 shares of BUD stock. So, your total investment is $315. In this example, if BUD reaches $50 by July 19, then you would realize approximately $239 in gains for a 75.9% return on capital invested.
Again, the longer you hold an Options Contract, the more time decay erodes potential gains.
What is Time Decay?
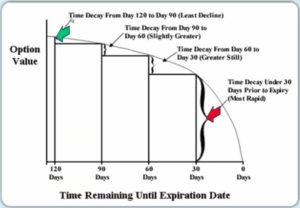
The time decay chart above shows you the rate of decline in value over a period of 120 days.
As you can see, the longer you hold an options contract, the faster the rate of decline in the value of the options contract.
So, when you buy an options contract, it’s important to check on the option regularly. If the price of the stock is not moving in the direction you anticipated, then the options contract can dramatically lose value or become worthless.
How Do I Get Started Trading Options?
- Choose an Online Broker – There are a wide variety of Brokers you can trade with starting with an investment of as little as $500. Some brokers include TD Ameritrade, Charles Schwab, TastyWorks, E-Trade, Fidelity Investments, Robinhood and many more.
Do your homework. Find the broker and trading platform that works the best for you. - Invest in Trading Education – This brief report barely scratches the surface of Options trading. There are multiple options trading strategies for bullish, bearish and sideways trading markets. There are strategies that are specifically designed to mitigate risk.
When you trade, you are putting your capital at risk. Learning about risk management, position sizing and finding a trading strategy that stacks the odds in your favor can improve your results. - Start with Paper Trading – Consider choosing a broker that has a demo platform that allows you to place trades in a simulated environment. You can place trades, exit trades and monitor your simulated profit and loss results.
Tip: Take paper trading seriously. The goal is to hone skills you can apply in a live account trading real money. If you can’t make money paper trading, then it might be time to reconsider your trading plan.